Planning and Scheduling
NetSuite provides the tools to easily plan your material supplies and schedule production for on-time delivery
Planning and Scheduling are often used together but understanding the relationship between them and how they interact is critical to the success of your business. NetSuite delivers the functionality you need to effectively plan your material purchases, position your inventory and schedule your employees, machines and work centers in production to make on-time delivery an achievable priority. NetSuite’s broad and tightly integrated business platform will help ensure that you achieve all of this through optimized business practices to ensure maximum profitability and customer satisfaction levels.
Features
Forecasting
NetSuite’s Demand Planning module offers several ways to calculate and predict demand based on historical demand, open opportunities and manually entered or imported sales forecasts. Whether you want the system to review monthly or weekly demand and generate forecasts using moving average, linear regression or seasonal average calculations you will have the ability to review and edit the forecasted demand before proceeding to supply planning. You can also have the system create demand based on sales forecasts.
Key Capabilities:
- Analyze Historical Demand
- Use Sales Forecasts
- Import from CSV, Web Services
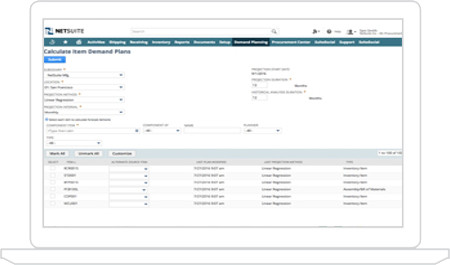
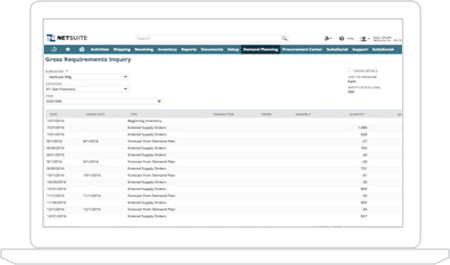
Material Requirements Planning
MRP is one of the standard methods for balancing demand and supply. NetSuite’s Demand Planning functionality provides the ability to explode BOM’s, check inventory and safety stock levels, review demand and analyze supply before generating planned orders. And it’s all done in the cloud with minimal overhead.
- Utilize the power of the cloud
- Generate planned orders
- Multi-location planning
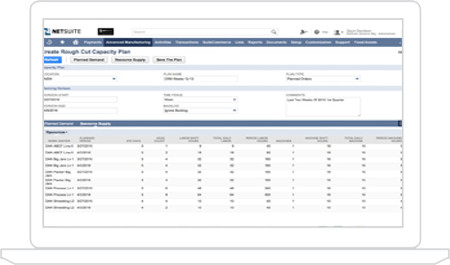
Capacity Planning
Production scheduling is one of the most critical elements of running a manufacturing facility, but is also one that is commonly done outside of a system because of the complexities involved with doing it accurately and with precision. The advanced scheduling engine can ensure availability of the most appropriate resource while generating a unique scheduling code that allows for advanced techniques such as light to dark sequencing.
- Multiple Constraints
- Scheduling Codes for sequencing
- Real-time updates from MES