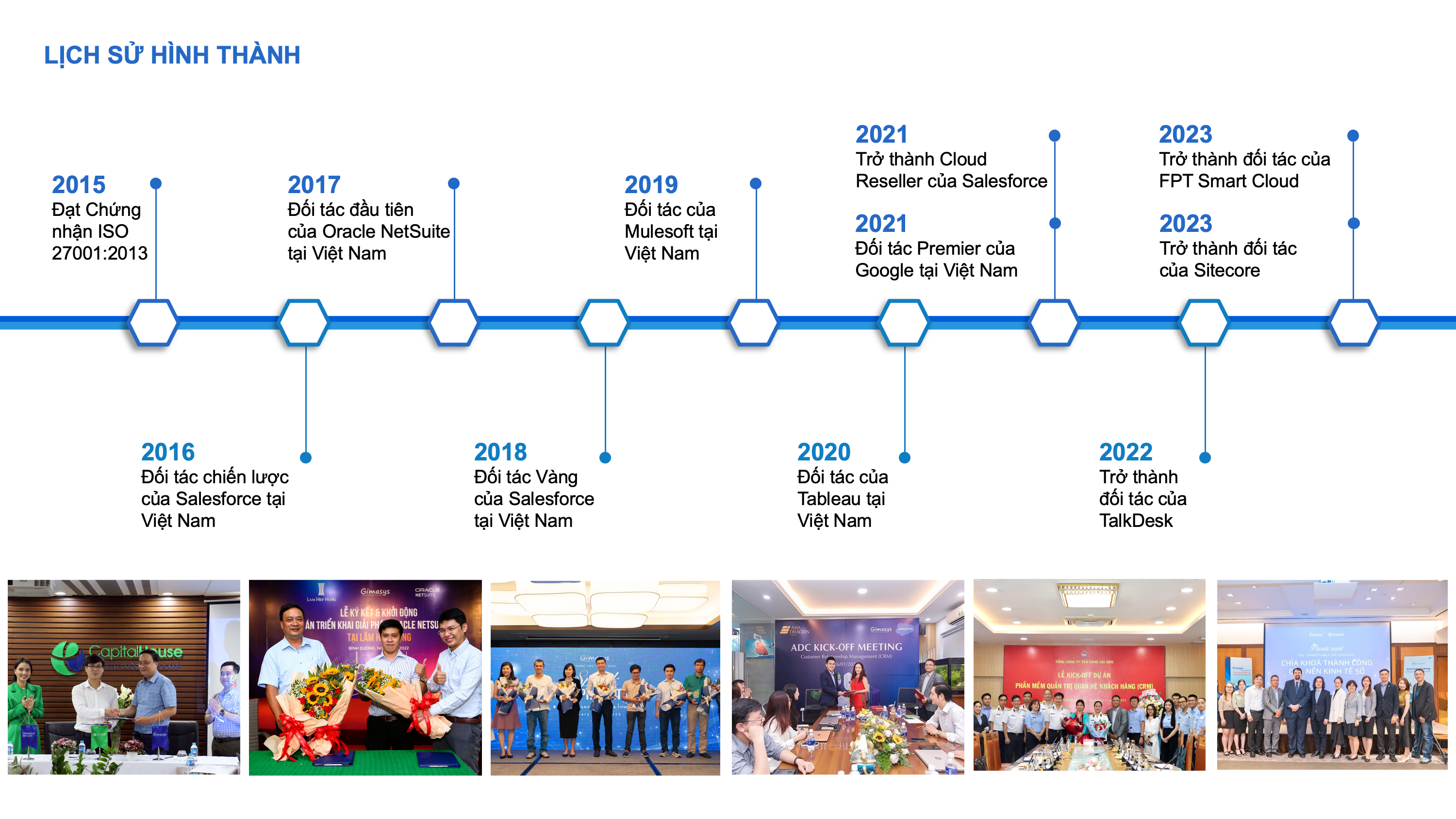
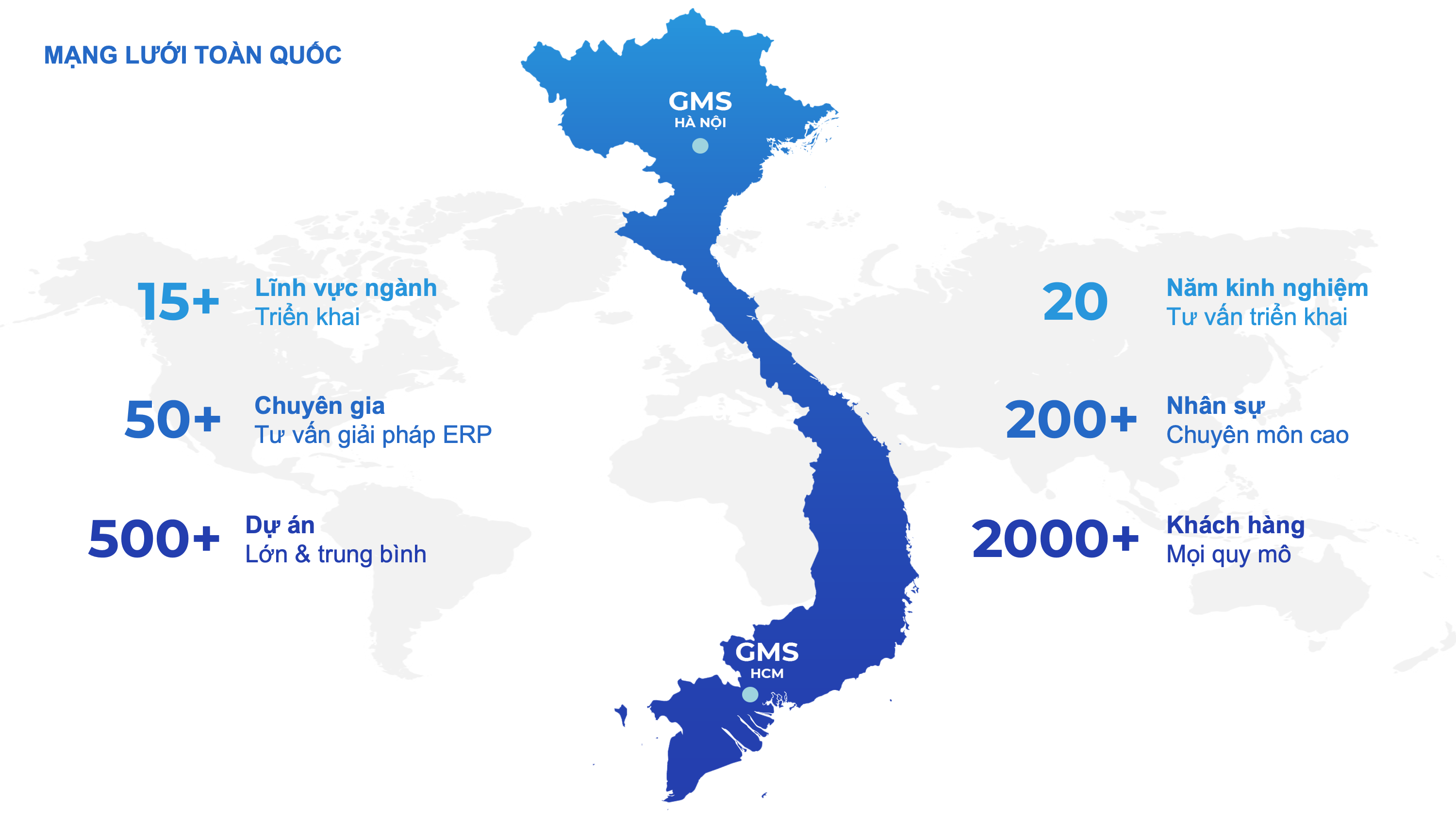
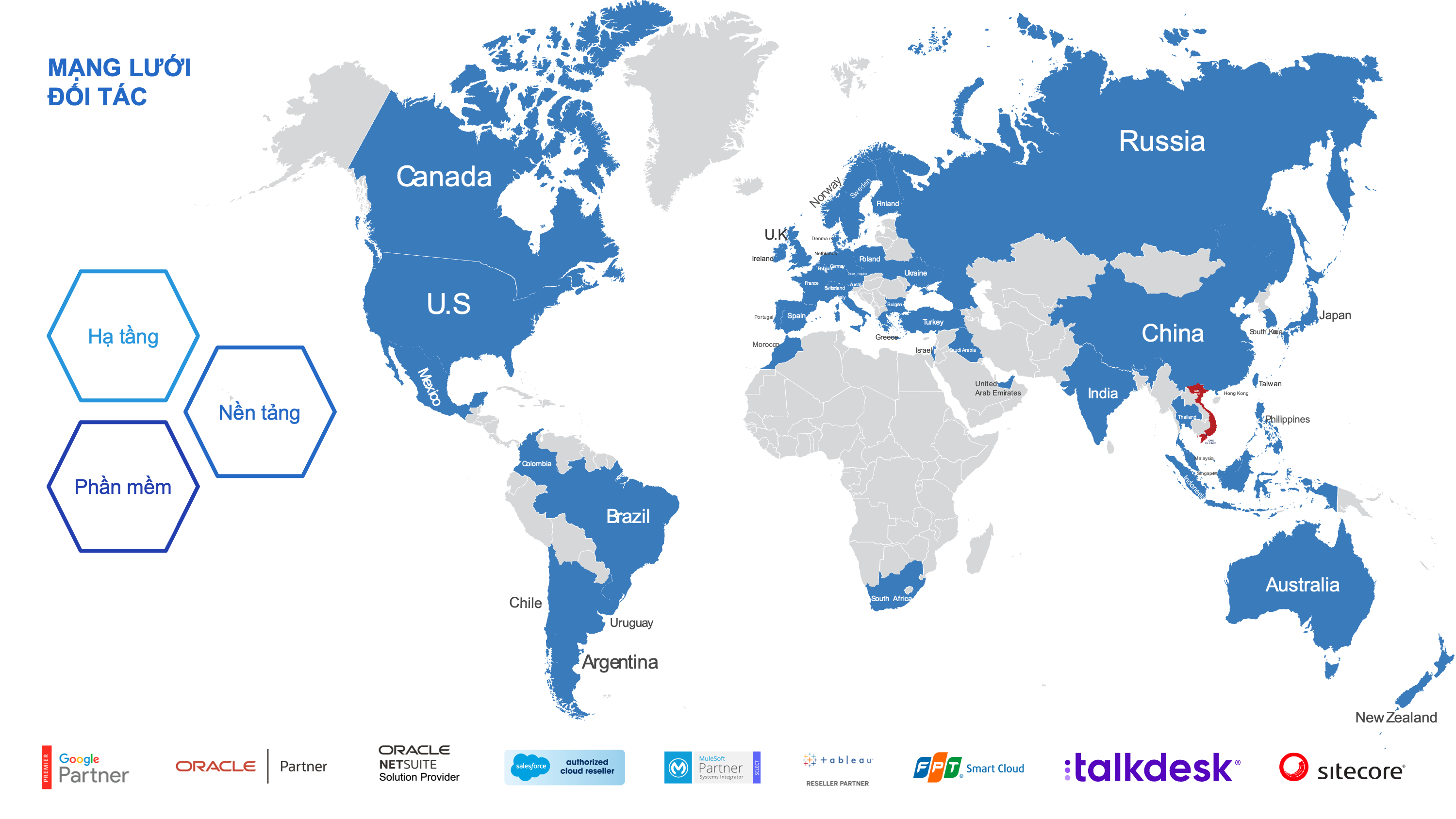
Supply Chain Execution
NetSuite makes it easier than ever to create, update and manage all of your purchase, transfer and work orders
Considering supply chain management as a whole, executing your plan is probably the most important phase and in a global economy, it can also be the most complex. When your manufacturing can take place on any continent and across multiple time zones, you need a simple but effective way to communicate with your distributors, partners, suppliers and contract manufacturers to make sure they know what you want and you know what they are intending on delivering.
Features
Supply Chain Control Tower
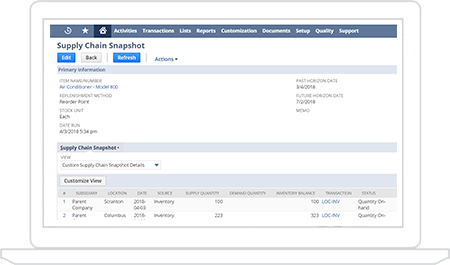
NetSuite has been working with customers to understand better how they run and monitor their complex supply chains. The Control Tower Snapshot provides a global time phase view that summarizes your current and future inventory position across our entire global supply chain.
This feature provides the ability to see projected inventory along with any demand or supply that affects it across a time horizon and throughout the supply chain in a way that makes it easy to identify potential issues.
Key Capabilities:
- Actively monitor your inventory, demand and supply across your entire global supply chain
- Time phased view to help identify future imbalances in demand and supply
- Filter results by Subsidiary and Location
- Drill-down into transactions to take action
- Export entire grid to excel for further analysis
Purchase Order Management
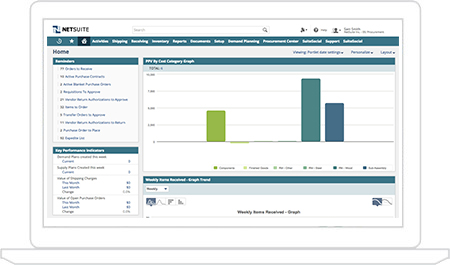
Creating and managing vendors, purchase orders, receipts and all other relevant transactions is one of the simplest, yet comprehensive aspects of the system. Vendors can be established and shared across all subsidiaries in your system to get a truly global view of your relationship. The Order items screen is the main place a user will go to monitor the list of orders that needs to be placed whether they are generated as a result of the supply planning process, blanket POs or reacting to re-order point parameters. In all cases if there is a purchasing contract in place, pricing will be automatically applied.
Key Capabilities:
- Simple Order Generation
- Approval Workflows
- Vendor Performance Tracking
Transfer Order Management
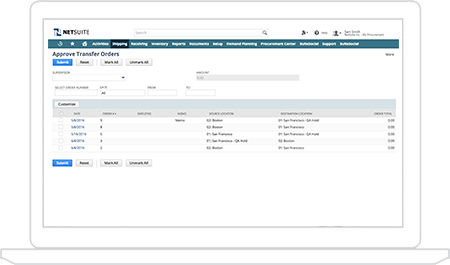
Whether you are using NetSuite as a single subsidiary or multiple, the ability to generate transfer orders between your company’s locations is critical to an efficient supply chain. Orders can of course be manually created on demand, but the real power of the system comes into play when using our distribution network functionality which will result in automatic planned or actual transfer or inter-company orders were necessary and with no additional effort.
Key Capabilities
- Track In-transit Inventory
- Full Automation Possible
- Inter-company Ready
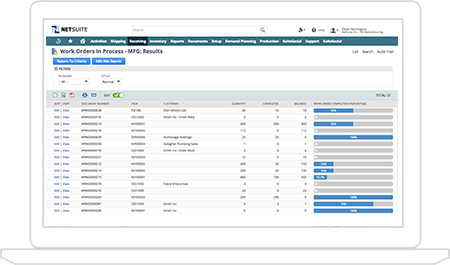
Work Order Management
Location Irrelevance is the essence of supply chain management in NetSuite. We believe that it shouldn’t matter where a product is made or who it’s being made by—you should expect the same level of information from the manufacturing process as if you were making it yourself. Work Orders are created and managed through the planning engine and across all locations and subsidiaries ensuring consistency and accuracy. Real-time updates are achievable through our cloud MES if desired.
Key Capabilities
- Easily Update Statuses
- Lot and Serial Traceability
- Constraint Management